- This feature is currently in Beta.
- You may expect updates, and changes to accessibility or pricing as we refine and enhance it.
What is the AI Advanced Search?
The AI Advanced Search is a powerful new way to find candidates within your database. It combines traditional filters with intelligent semantic search to deliver faster, more accurate results.
This enhanced tool gives you greater flexibility and control, assigning a relevance score to each candidate based on how closely they match your query. That means you can instantly zero in on the most suitable profiles without sifting through endless results.
How to Use AI Advanced Search Criteria
When searching for candidates, the AI Advanced Search offers two powerful options: Filters and Semantic Criteria. You can add, remove, or adjust criteria based on the candidates returned in your search results.
Filters vs. Semantic Criteria: What’s the Difference?
Filters
Filters allow for precise, rule-based searches and are ideal for setting exact values or ranges (eg. location is X, salary less than Y). Use these to define exact requirements such as:
Education
- Degree – eg. Bachelor’s Degree
- School Country – eg. US
Experience
- Employer – eg. Airbus
- Job Location – eg. New York, US
- Years of Experience – eg. More than 5 years
- Job Hopper Status – eg. Must not be a job hopper
Candidate Details
- Age – eg. Over 18
- Current Location – eg. New York, US
- Gender – eg. Female
- Nationalities – eg. French
- Languages – eg. English
Salary
- Expected Salary – eg. Less than $180,000/year
ATS Details
- Resume – eg. Has resume
- Candidate Owner – eg. Alex Moss
- Tags – eg. Available
Semantic Criteria
Semantic Search uses AI-powered contextual matching to identify candidates with related experiences, even if the wording isn’t an exact match.
Skills
- Skills - eg. UX Design, UI Design
Education
- School Name – eg. MIT, Stanford University
- Specialization – eg. Digital Media Design, Computer Science
Experience
- Job Title – eg. UX Designer, Frontend Engineer, Product Manager
- Job Industry – eg. Aviation, Healthcare, E-commerce
- Work Experience – eg. Start-Up, Corporate, Freelance
By combining both Filters and Semantic Criteria, you can conduct searches that are both targeted and flexible, ensuring you don’t miss highly relevant candidates just because they describe their skills, role, or backgrounds a little differently.
Tips
| If you want to... | Use... |
|---|---|
| Only see candidates from a specific city | Filter |
| Only see candidartes with 5+ years of experience | Filter |
| Only see candidates who speak English | Filter |
| Find candidates with similar skills or roles | Semantic Criteria |
| Include people with related job titles | Semantic Criteria |
| Explore different ways candidates describe a skill | Semantic Criteria |
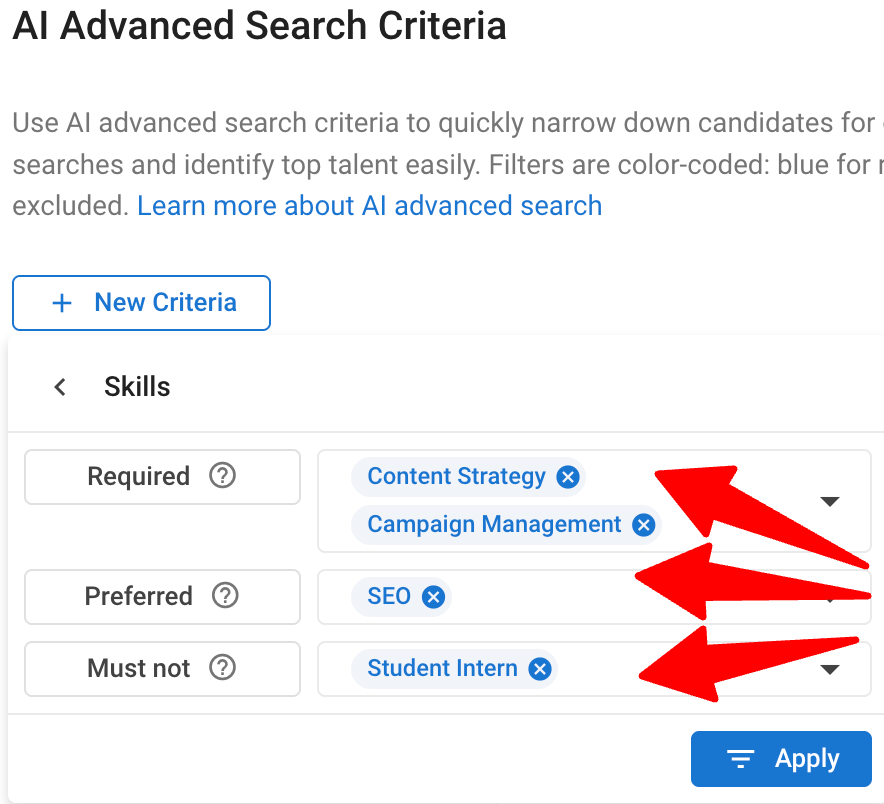
How to Use Required, Preferred, and Must Not Criteria
When refining your search, you can prioritize or exclude specific candidate criteria by marking it as Required, Preferred, or Must Not. This helps you tailor your results to match your priorities more accurately.
- Required (Must-Have)
- Use this for criteria that candidates must meet to appear in your search results.
- If a candidate doesn’t meet this condition, they’ll be excluded from the results.
- Example:
- Required Skill: Campaign Management
- Result: Only candidates with this skill will appear
- Example:
- Preferred (Nice-to-Have)
- Use this for criteria that are desirable but not required.
- Candidates who match preferred criteria will receive a higher relevance score, improving their position in the results.
- Those who don’t match can still appear in the list.
- Example:
- Preferred Skill: SEO
- Result: Candidates with SEO will rank higher, but those missing SEO will still be shown
- Must Not (Exclude)
- Use this to filter out candidates with specific attributes from your results.
- Anyone matching this criterion will be excluded entirely.
- Example:
- Must Not for Job Title: Intern
- Result: Candidates with “Intern” in their job titles will not appear
How to Conduct a Search
- Head to the following page. Alternatively, click on "Candidates" from your side menu and then the "AI Advanced Search" tab.
-
Click on "Criteria".
-
In the AI Advanced Search Criteria panel, choose the filters and semantic criteria you want to apply.
-
Click “Apply” to view results matching your selected criteria.
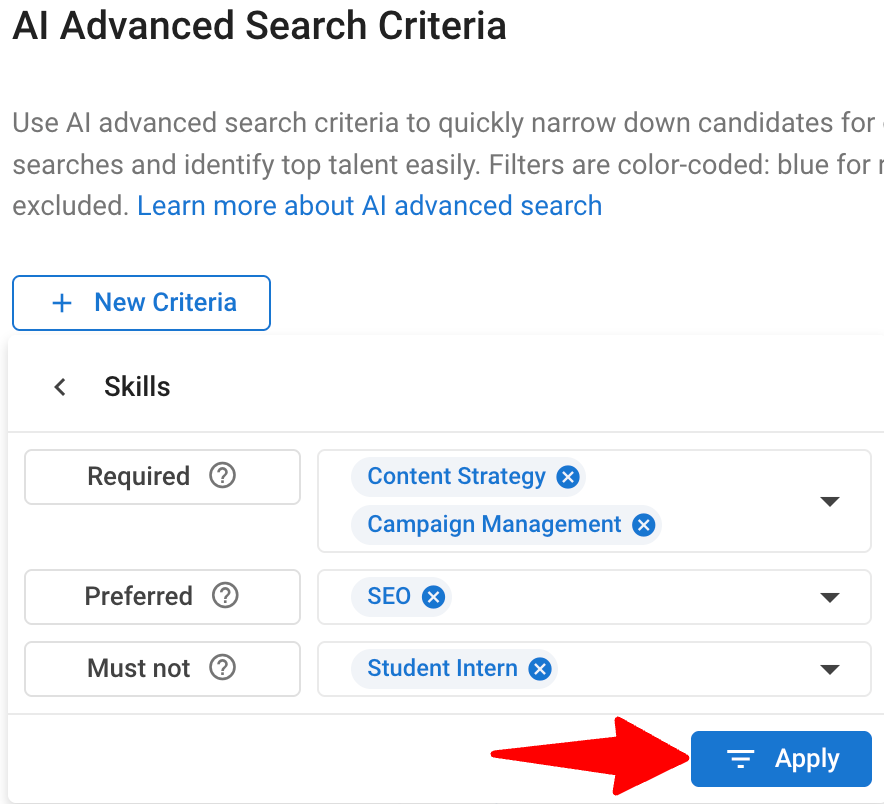
-
You can add multiple criteria to refine your search further.
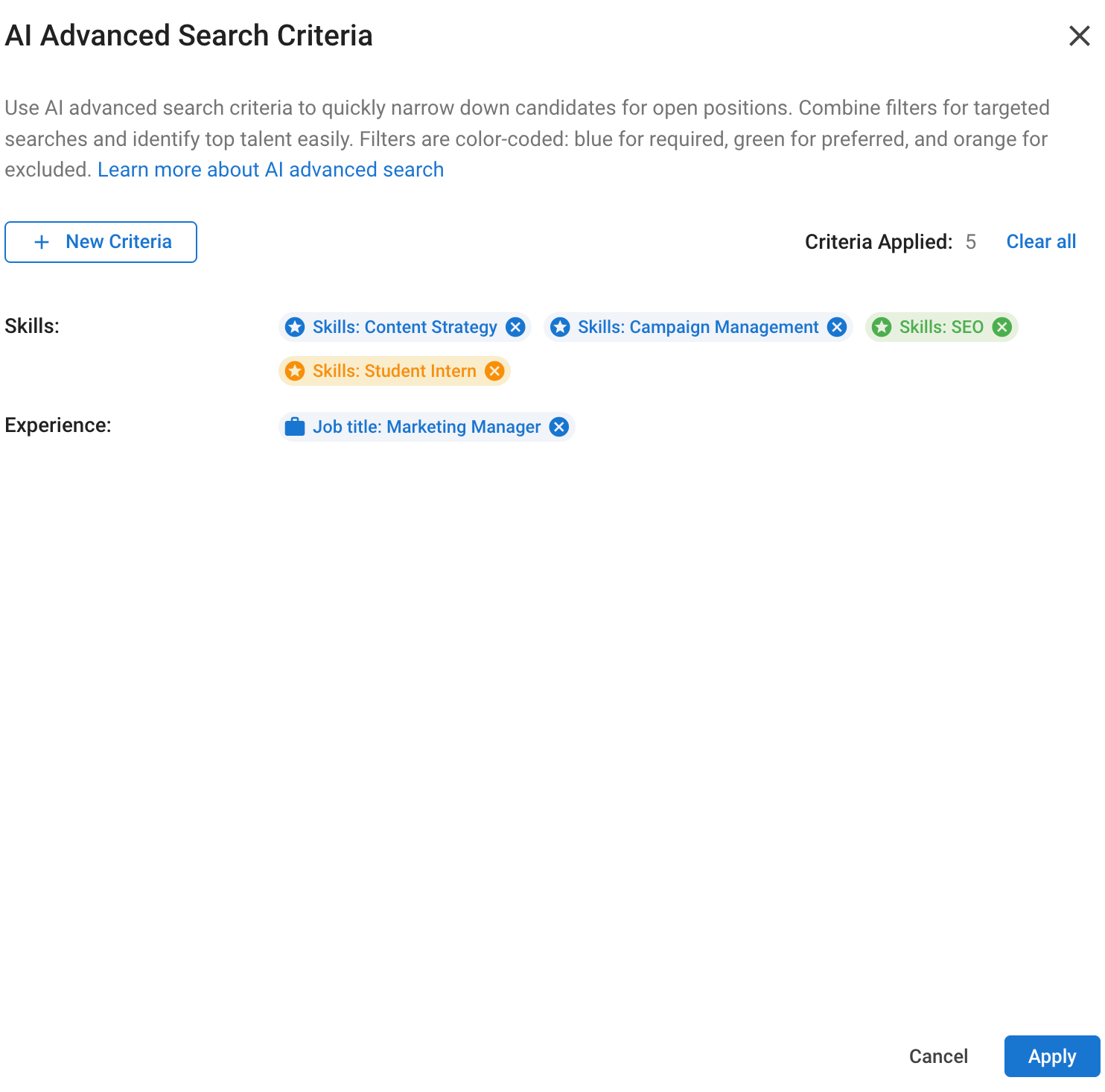
-
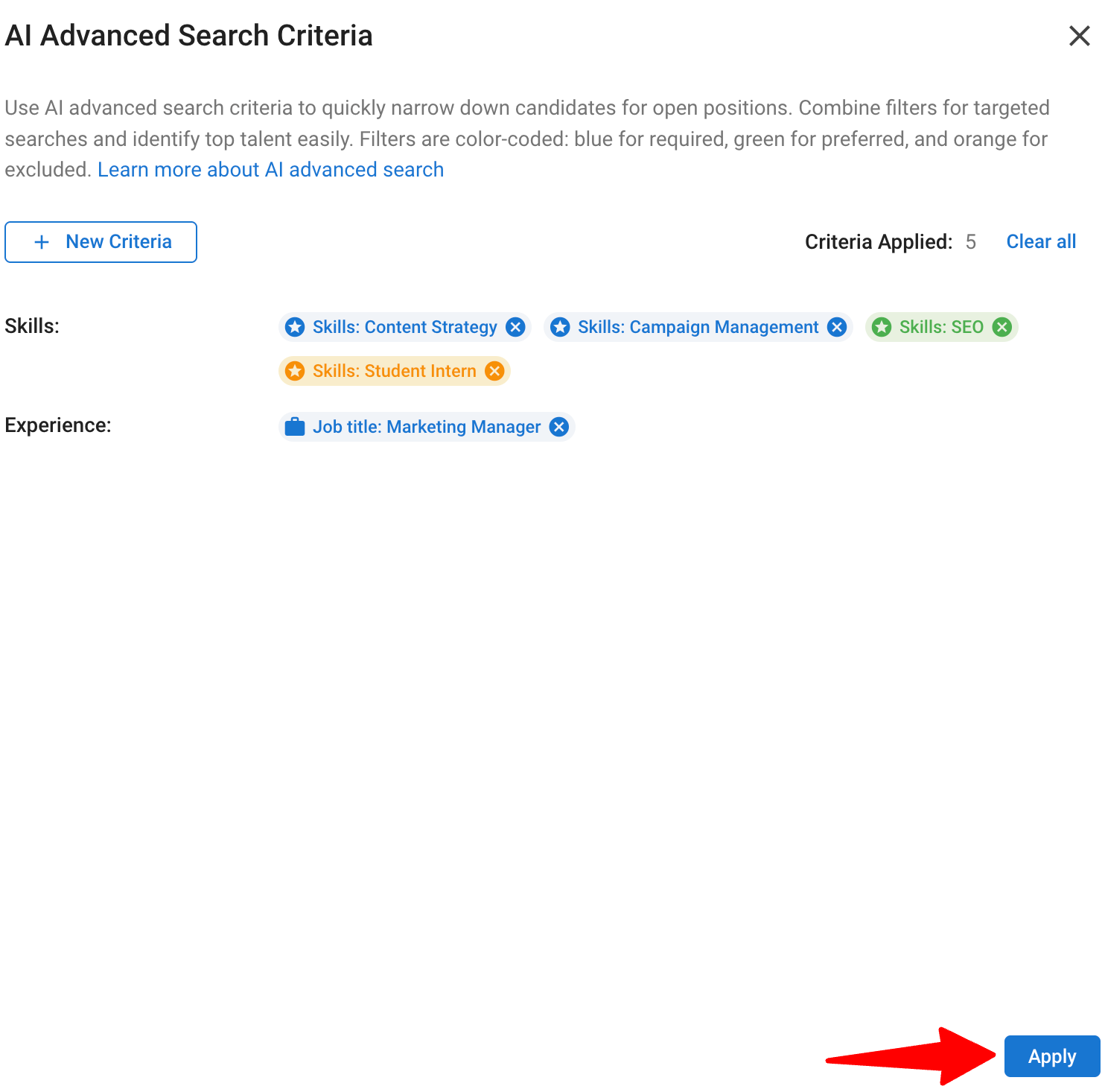
Once you’ve finalized your criteria, click “Apply” at the bottom of the panel to launch the search.
Best Practices for Using AI Advanced Search with Semantic Criteria
1. Start broad, then Refine your search.
- Begin with general terms. The AI will interpret the meaning and return related profiles.
- Example:
- Skill: “UX Design”
- Results: May include candidates with roles like Interaction Designer, Product Designer, or User Experience Specialist
2. Combine semantic criteria with filters for accuracy.
- Use semantic search to explore related profiles and filters to enforce strict requirements like location, experience, or language.
- Example:
- Semantic: “Frontend Developer”
- Filters: Location = Paris, Experience = 5+ years
3. Experiment and Iterate.
- Not getting the ideal results? Try:
- Using synonyms or simpler terms
- Simplifying your inputs
- Adding variations to expand the scope
4. Understand the Limits for semantic criteria.
- You can apply up to:
- 20 Skills
- 3 Specializations
- 5 Industries
- 5 Work Experience Types
- 5 Job Titles
- 5 School Names
- We do not have any limit on the number of filters
- You can still use Boolean search in the main search bar to further refine your results using keywords.
What is a boolean string?
A boolean search is a specific type of search allowing users to combine keywords with operators like AND, NOT and OR to make the search results more relevant. Manatal's boolean search works the same way as Linkedin or Google.
Manatal's boolean search is based on data parsed from candidate resumes, social media (i.e. Linkedin profile,...), fields in candidate profiles and candidate tags.
Boolean search operates on the following 5 elements:
- AND - Search for profiles containing term A AND term B
- OR - Search for profiles containing term A OR term B
- NOT - Search for profiles NOT containing term A
- () - Search for profiles containing (term A AND term B)
- "" - Search for profiles containing "term/phrase A"
These elements help separate and group results based on the specific traits you're searching for. Combining them in your Boolean search narrows profiles down based on relevance.
Operators AND, OR and NOT must always be written in capital letters.
How to interpret results
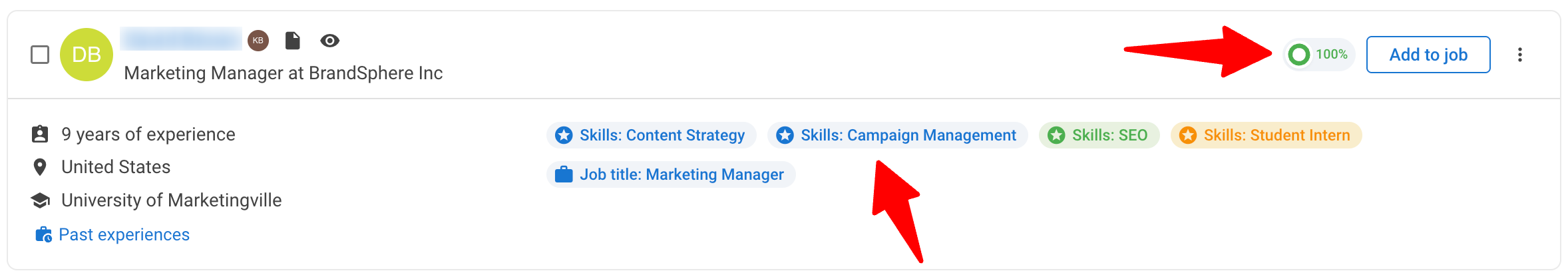
- Each candidate’s profile highlights the criteria that matches with your search, with a color-coded system indicating the relevance of each match.
- The recommendation score reflects the percentage match between the candidate and your search, making it easy to identify the most suitable profiles at a glance.
How to understand the scoring?
- The recommendation score shows the percentage match between the candidate and your search criteria, helping you quickly spot the most relevant profiles
- It displays as a percentage to give you a clear, at-a-glance view of relevance
- We evaluate key criteria like skills, job title then combine them into one overall score
- Candidates who meet or exceed the relevance threshold, will appear in your search results
- Candidates who don’t meet the relevance threshold, won’t appear in your search results
What languages are supported?
The feature supports cross-language queries and the following languages:
- Afrikaans
- Albanian
- Amharic
- Arabic
- Armenian
- Assamese
- Azerbaijani
- Bashkir
- Basque
- Belarusian
- Bengali
- Bosnian
- Breton
- Bulgarian
- Burmese
- Catalan
- Cebuano
- Chinese
- Corsican
- Croatian
- Czech
- Danish
- Dhivehi
- Dutch
- English
- Esperanto
- Estonian
- Faroese
- Finnish
- French
- Galician
- Georgian
- German
- Gujarati
- Haitian
- Hausa
- Hebrew
- Hindi
- Hungarian
- Icelandic
- Indonesian
- Irish
- Italian
- Japanese
- Javanese
- Kannada
- Kazakh
- Khmer
- Kinyarwanda
- Kirghiz
- Korean
- Kurdish
- Lao
- Latin
- Latvian
- Lithuanian
- Luxembourgish
- Macedonian
- Malagasy
- Malay
- Malayalam
- Maltese
- Maori
- Marathi
- Modern Greek
- Mongolian
- Nepali
- Norwegian
- Norwegian Nynorsk
- Occitan
- Oriya
- Panjabi
- Persian
- Polish
- Portuguese
- Pushto
- Romanian
- Romansh
- Russian
- Sanskrit
- Scottish Gaelic
- Serbian
- Sindhi
- Sinhala
- Slovak
- Slovenian
- Somali
- Spanish
- Sundanese
- Swahili
- Swedish
- Tagalog
- Tajik
- Tamil
- Tatar
- Telugu
- Thai
- Tibetan
- Turkish
- Turkmen
- Uighur
- Ukrainian
- Urdu
- Uzbek
- Vietnamese
- Waray
- Welsh
- Western Frisian
- Xhosa
- Yiddish
- Yoruba
- Zulu
FAQ
1. What is semantic search?
- Semantic search finds candidates based on meaning, not just keywords. For example, if you search for "UX Designer," it might also return "Product Designer" or "Interaction Designer" if they match in context.
2. When should I use Required, Preferred, or Must Not?
- Required: Use for must-have criteria. Candidates must meet this to appear in results. (e.g., location = Paris)
- Preferred: Use for nice-to-have attributes. Matching candidates rank higher, but others can still appear. (e.g., experience in startups)
- Must Not: Use to exclude candidates with specific attributes. (e.g., job title = intern)
3. Can I combine filters and semantic search?
Yes! That’s the power of the AI Advanced Search. You can use filters to define strict criteria and semantic search to surface broader, relevant matches.
4. How is the match score calculated?
Each candidate gets a recommendation score based on how well they match your Required and Preferred criteria. The more they match, the higher the score will be.
5. What is Private Beta? Can I share feedback?
Private Beta means this feature is available to a select group of users for testing. We're gathering feedback to refine it before the full public launch.
6. Is the AI Advanced Search GDPR friendly?
You can refer to Manatal AI terms in the terms and conditions here.
7. What AI model are we using?
We are using one of latest gen AI model using LLM for our semantic search.